In the image above, SLED/M provides a visualization of a methane leak at a compressor station
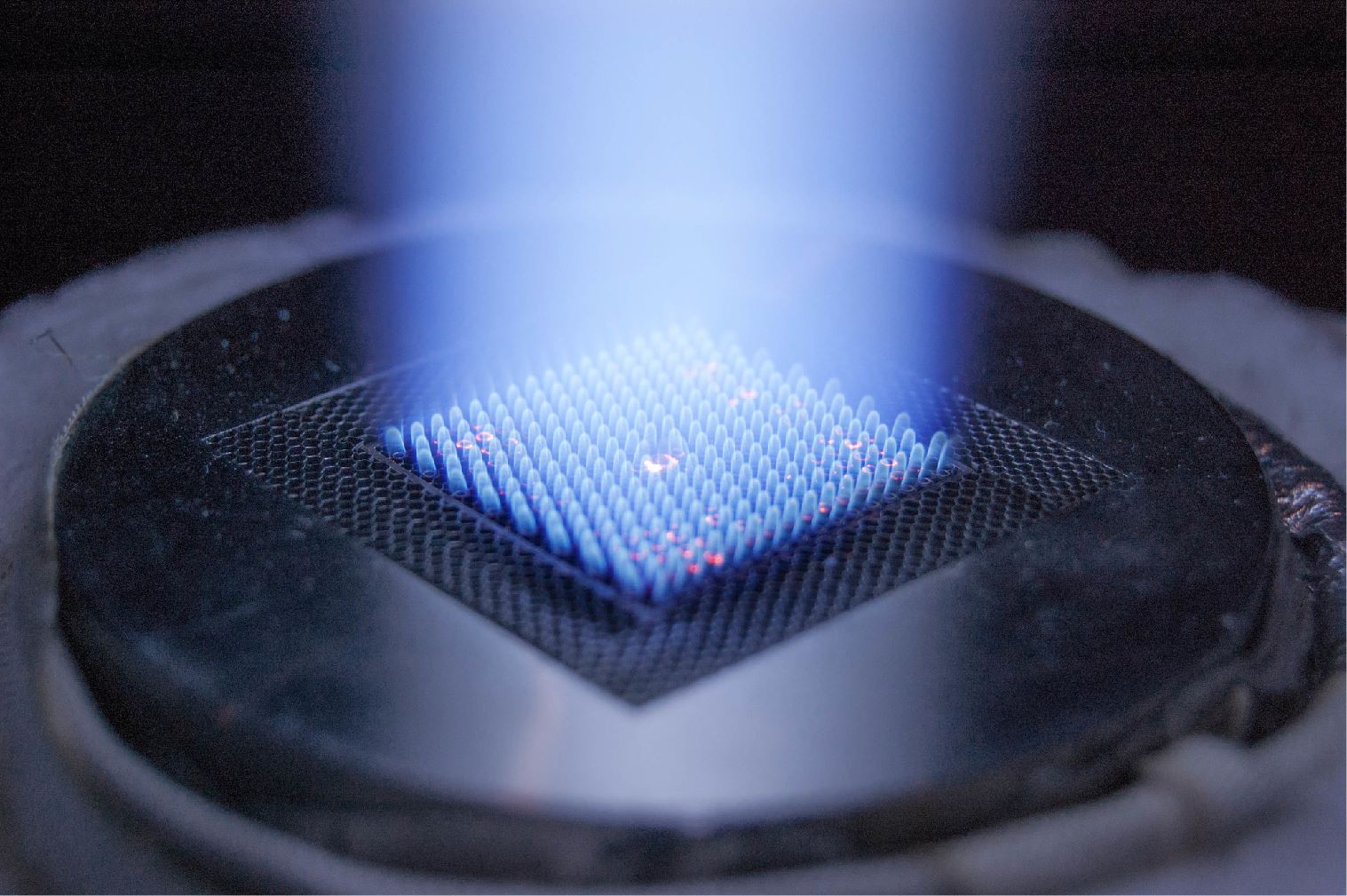
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with support from NETL, has concluded a five-year project resulting in the development of a novel methane leak detection technology that has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the energy sector.
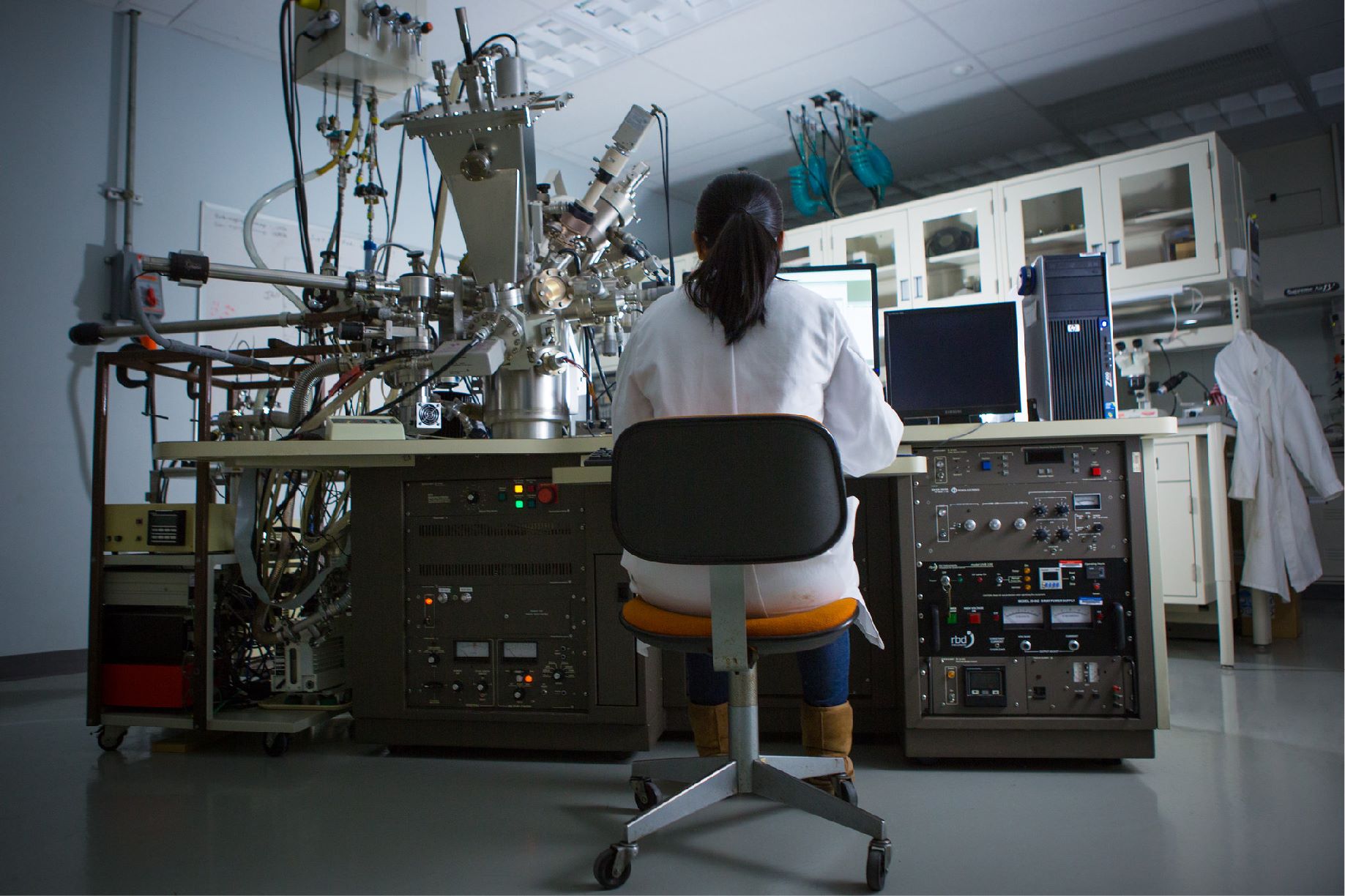
NETL researchers, working closely with experts at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO), have designed a multi-cloud-based computational solution to complement on-site resources that will accelerate clean energy research across the agency.
NETL’s Strategic Systems Analysis & Engineering (SSAE) researchers and analysts are pursuing an all-hands-on-deck effort to realize a clean energy future by harnessing the nation’s fossil energy resources to produce hydrogen sustainably through the use of commercial and advanced hydrogen production and carbon dioxide capture technologies.
Fossil fuel-derived hydrogen (H2) presents new opportunities to decarbonize challenging sectors of the economy, such as transportation and decentralized, distributed industrial applications.
The January 2022 edition of the RWFI E-Note Monthly, the newsletter of NETL’s Regional Workforce Initiative (RWFI), will include invitations for an upcoming webinar on the job-creating potential of hydrogen power.
The image above shows a modular container unit with Polaris membrane stacks. The CEMEX project will have multiple containers. Credit: Image provided by Membrane Technology & Research Inc.
NETL’s industry partners are evaluating the use of a transformational membrane technology to capture greenhouse gas produced during the manufacturing of cement and lower the environmental footprint for this important building and construction material.
Above: Phil Reppert training at RAX Run Eventing in Northern Virginia with Glory’s Gold, a Hanoverian horse.
In addition to his work as NETL’s Associate Director for Geological and Environmental Systems, Philip Reppert, Ph.D., has demonstrated a profound talent for horsemanship and storytelling, recently combining these two passions into writing projects, including a family-friendly novel with a message of hope during the holiday season.
The January 2022 edition of the SSAE Newsletter provides updates about recent research initiatives undertaken within NETL’s Strategic Systems Analysis and Engineering (SSAE) directorate.
Click here to access this latest edition and learn about activities that SSAE is leading to gain insights into new energy concepts, support the analysis of energy system interactions and advance its capabilities.
Highlights in this edition include:
The Energy & Geoscience Institute (EGI) at the University of Utah and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy’s (EERE) Geothermal Technologies Office (GTO) have partnered with NETL to explore enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) via the Utah FORGE project. Once optimized and developed, electricity from EGS could power tens of millions of American homes and businesses.
As the nation’s energy sector moves toward an emissions-free future, fuel flexibility and successful integration of renewable resources will be more important than ever in designing the next generation of power plants. NETL research in energy conversion engineering (ECE) is enabling researchers to understand what will comprise the advanced energy systems of tomorrow, pioneering innovation in low-carbon power production to meet the Biden Administration’s goals of a net-zero emissions power sector by 2035 and broader economy by 2050.
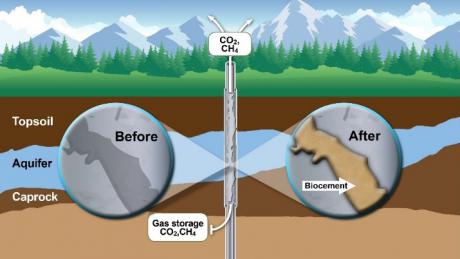
The image above illustrates MICP formation in a wellbore cement defect and leakage pathway. The resulting mineral seal mitigates leakage to aquifers and the atmosphere. Reprinted from the International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, Vol 86.