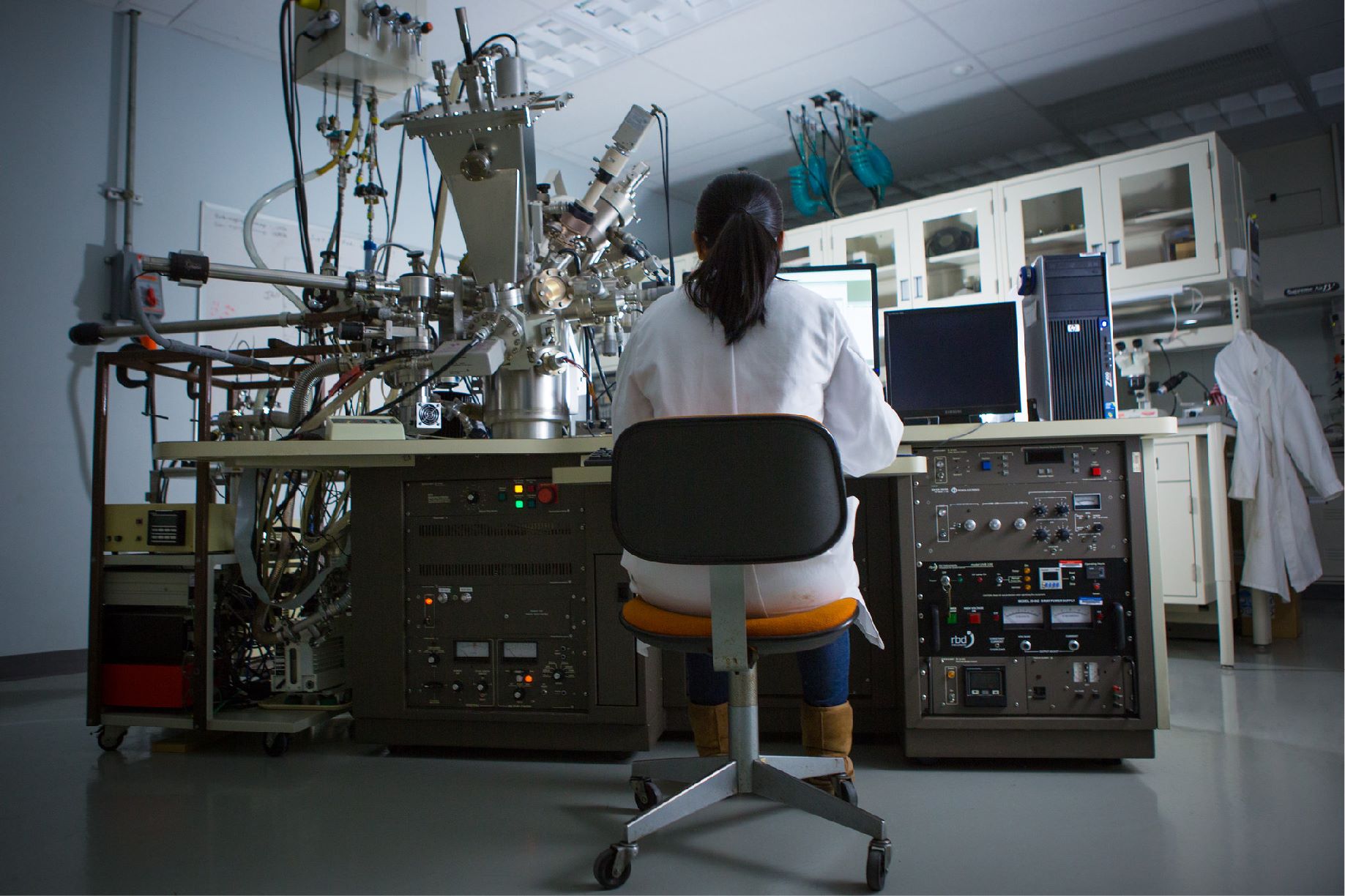
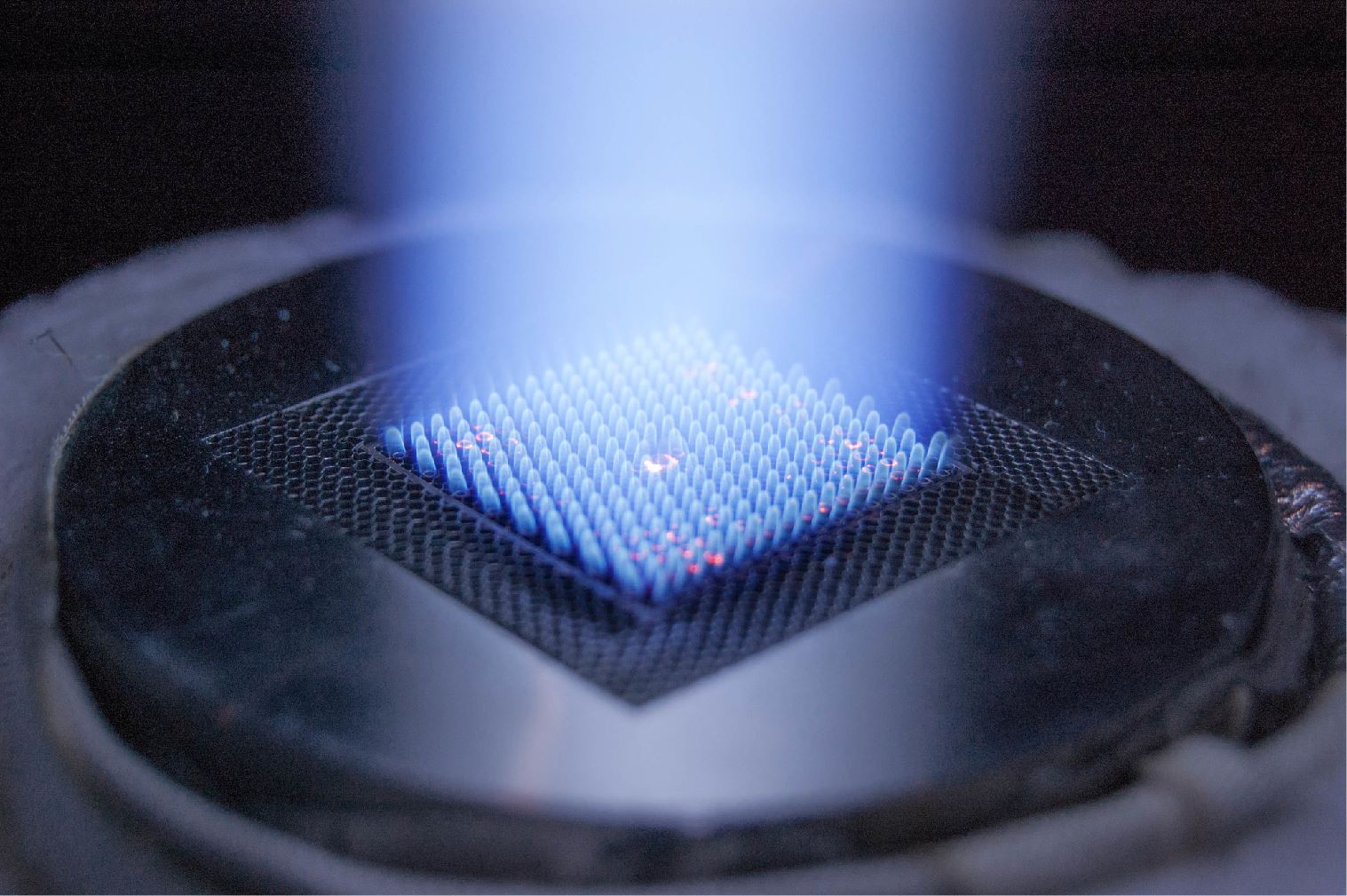
NETL, the nation’s only National Laboratory dedicated to fossil energy research, today launched a new website that highlights the Laboratory’s mission, research news, educational offerings, core competencies, business opportunities, and technologies available for commercialization.
The new website, https://netl.doe.gov/, offers access to the latest research information generated by the Laboratory on oil, coal, natural gas and other energy topics as well as posts about NETL’s work by news organizations from around the nation.
About
News and Events
Research and Programs
Carbon Management Point Source Carbon Capture Carbon Dioxide Removal Carbon Dioxide Conversion Carbon Transport & Storage Hydrogen with Carbon Management
Resource Sustainability Methane Mitigation Technologies Minerals Sustainability Natural Gas Decarbonization and Hydrogen Technologies Advanced Remediation Technologies Energy Asset Transformation
Key Lab Initiatives Advanced Alloys Signature Center (AASC) Science-based Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Institute (SAMI) Center for Microwave Chemistry (CMC) Center for Sustainable Fuels and Chemicals (CSFC)
Energy Technology Development Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Battery Workforce Initiative Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response Office of ElectricityGrid Resilience
Business
Library
Explore our Library

Approved Categorical Exclusions Environmental Assessments Environmental Impact Statements Oil and Gas Projects Summaries NETL Fact Sheets NETL Newsletters Publication Search Energy Data Exchange (EDX) FECM External R&D Final Technical Reports Summary Information for External R&D Awards Technical Reports Series (TRS) Peer Review Reports Interagency Working Group Initial Report
- Research and Programs
- Carbon Management
- Core Competencies
- Resource Sustainability
- University Training & Research
- Key Lab Initiatives
- Energy Technology Development
- Featured Infrastructure
- Methane Emissions Reduction Program
-
- Business
- Technology Transfer
-
- Library
- Energy Analysis
-
- About
- News and Events
- Education