With 6 percent of the Nation’s prospective petroleum on reservations, Native Americans could play a key role in domestic energy policy and development. But this has been hampered because many tribes have been forced to rely upon non-Indian companies for development and exploration. This has meant that tribes have been passive royalty owners, not participants in value-added activities such as exploration, production, or refining. The key to moving tribes into an active role in the development of tribal resources is building up tribal technical and business expertise. Another important aspect of this problem is to provide the tribes with additional revenues and incentives to expand their role as an active partner or leader in the development of tribal resources. For a number of reasons, many prospective areas or existing fields on Native American and Alaska Native Corporation lands are underexplored or underdeveloped. One problem has been a lack of exposure to and technical training in cutting-edge, innovative technology that is increasingly applied by major oil companies only to large fields or fields outside the United States, making it more difficult for domestic companies and tribes to learn about and become proficient in these new technologies.
The project directly addresses these problems. The project applies state-of-the-art seismic technology and characterization technology not previously applied to algal mound plays in the Paradox Basin to benefit the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe through incremental financial increases and enhancing the technical prowess of the Red Willow Production Company, a wholly owned Native American company. Beyond the important aspect of equipping the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe and other Native Americans to take a leadership role in developing their resources, the project will directly benefit the domestic petroleum industry that still struggles with exploration for algal mound prospects in the Paradox Basin and elsewhere and experiences recovery factors on the order of 20%.
Results
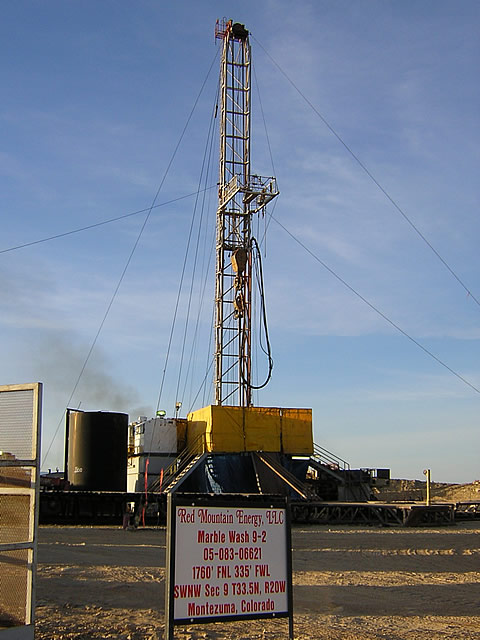
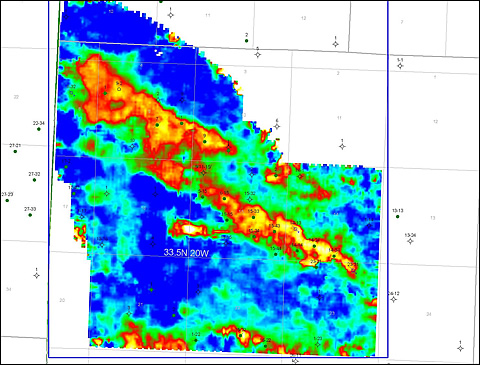
The first well, Marble Wash 9-2, located from the seismic data in the northwestern portion of the project area, was brought on production in late April 2006 and is still producing modest amounts of oil. Additional drilling locations were selected but have not yet been drilled. The multicomponent seismic data interpretation was completed. Analyses of the multicomponent data showed statistically significant relationships between the internal reservoir properties of the producing horizons and the multicomponent attributes. These relationships have been used to construct a static model of the project area for input into a dynamic simulation. The dynamic simulation will provide the final evaluation as to the potential for using multicomponent data for imaging internal reservoir parameters of the algal mounds and similar drilling targets.
Benefits
This work is being performed on the Roadrunner/Towaoc fields of the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe, located in the southwestern corner of Colorado. This project has already benefited the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe through increased oil revenues and has enhanced the technical capabilities of the Red Willow Production Company, a wholly owned Southern Ute Tribe entity. The statistically significant relations between the multicomponent attributes and the internal reservoir parameters such as net porosity of the pay zones, clay content, water saturation, net to gross and other reservoir parameters, if validated by the dynamic modeling, will provide a methodology for explorationists and reservoir geologists in the Paradox Basin and elsewhere to develop more accurate reservoir models on which to base field development decisions, and to aid explorationists in high-grading drilling opportunities.
Summary
Among the project’s milestones, researchers achieved the following:
- Red Willow expanded P-wave coverage and upgraded its survey to a state-of-the-art 3-D, 9-C survey from the original 3-D, 3-C survey at Red Willow’s expense.
- The first 3-D, 9-C data were acquired and processed for an algal mound play.
- Multivariate statistical analysis of P-wave data showed good correspondence to mapped lithostratigraphy in wells and productivity.
- P-wave-derived isopachs were used for selecting well locations.
- The first well, Marble Wash 9-2, was drilled and tested.
- Five additional well locations were selected based on multicomponent interpretation results.
- Statistically significant multivariate regression models relating the multicomponent attributes to internal reservoir parameters have been developed, which represents in new step forward in the use of multicomponent data for interpreting the internal properties of reservoirs.
- A static model, based on the seismic attributes, has been developed for the project area
Recent advances in seismic acquisition and processing offer new ways to see smaller features and to characterize the internal structure of the reservoirs. In order to apply advanced seismic methods, it is necessary to develop an understanding of and calibration between the seismic response of these algal mounds from multivariate analysis of conventional 3-D seismic data and the internal structure of the mounds, which may be revealed by the shear wave component. A key to increasing the effectiveness of exploring for the algal mounds with seismic data is to calibrate the seismic response over a known reservoir.
Shear wave data have the potential to differentiate between subtle changes in lithology and fluid-filled porosity, as shear wave velocity is sensitive to the presence or absence of fluids. The use of multicomponent data (shear waves) has been demonstrated to be a useful tool to discriminate between lithology types in carbonate environments. Notably, diagenetically altered dolomites are more porous (and possibly fractured) than the surrounding limestones and result in good hydrocarbon reservoirs. These have a significantly different shear-wave velocity that can be exploited and identified using Vp/Vs analyses of multicomponent data.
Shear waves also may be of value for discriminating algal mounds, based on the lithology and/or fracture content associated with their development. Although P-waves have proven successful in this project for locating the algal mounds, they do not provide as much information on the internal structure: porosity, fracture, and fluid changes. Shear waves can provide additional petrophysical constraints to help identify such variations in the reservoir rock. The S-wave calibration to the lithology was accomplished by acquiring a vertical seismic profile to determine the S-wave velocities and then tying the S-wave data volume back to the reservoir formation.
Recent advances in conventional 3-D seismic data have shown that there is a considerable change in P-wave velocity as a function of direction. Conventional 3-D imaging has dramatically improved by applying anisotropic stacking velocities, and as a by-product, anisotropic velocity data volumes are produced. These velocities are thought to be influenced by stress, and stress is thought to be an influence on permeability. However, the technology has not been applied in a reservoir setting, so the connection between the seismic response and the reservoir performance has not been quantified. A second outcome of including azimuthal velocity variation during processing is that directional amplitude vs. offset (AVO) analysis has been improved, providing a link to S-wave information within conventional P-wave data. The value added by AVO processing will be assessed to determine if lithology can be predicted from this response.
This project has demonstrated that the multivariate modeling of multicomponent data can yield more accurate assessment of external mound geometry and internal mound reservoir properties than conventional approaches involving cross-plotting or mapping of single attributes.