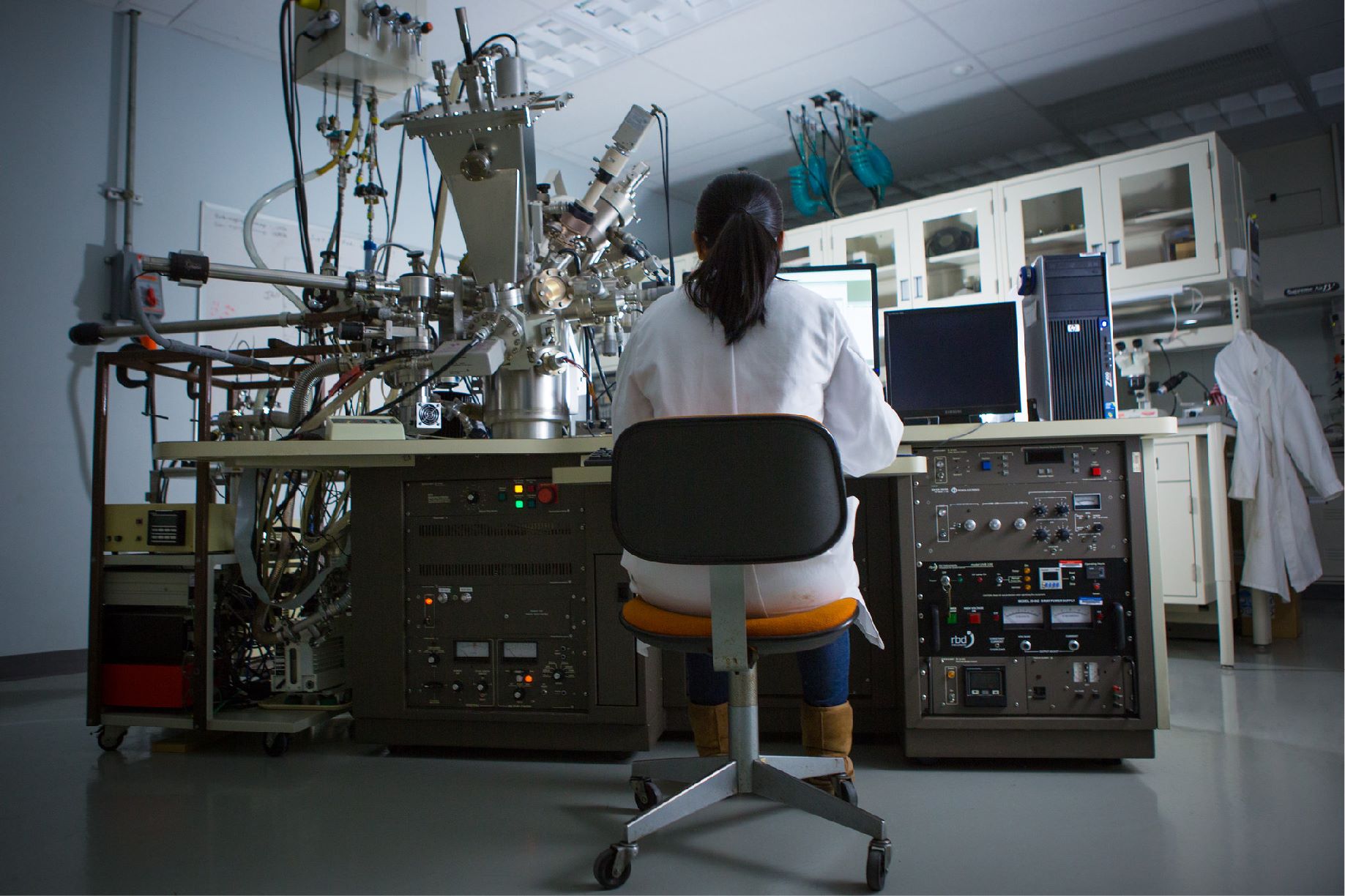
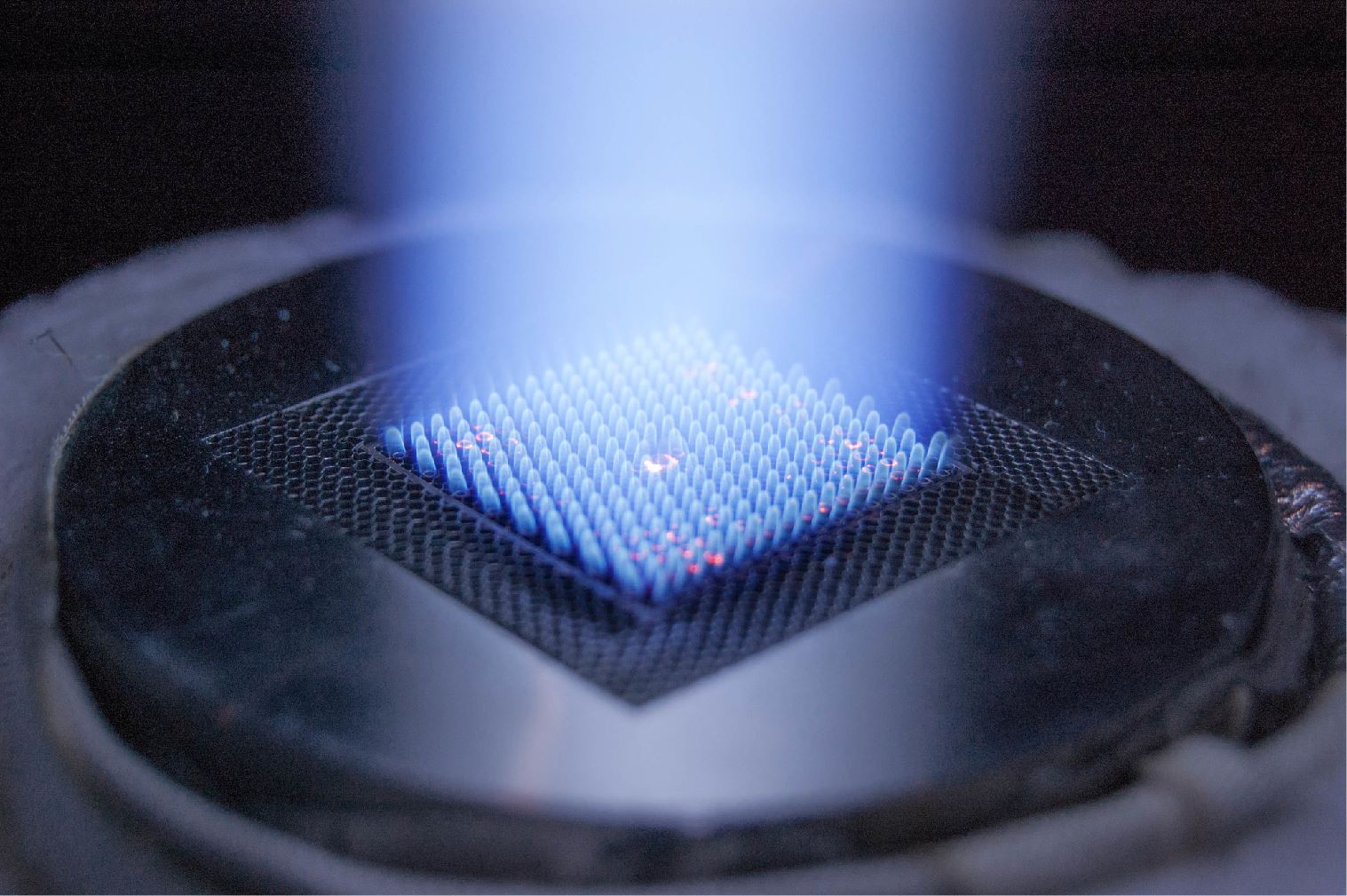
An NETL-supported project, which could offer a path to lower-cost power generation, has successfully demonstrated a supercritical turbine technology in a pilot plant that can produce enough power to supply electricity to approximately 4,000 homes — the largest scale demonstration of the technology ever accomplished.
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management (FECM) today announced $6 million for one selected project to explore the transport of carbon dioxide (CO2) from onshore industrial and power generation facilities to offshore secure geologic storage in Texas state waters. In addition, DOE announced it will make up to $48M available under the fourth opening of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law funding opportunity to support regional CO2 transport networks that connect sources of CO2 to locations for geologic storage or conversion to value-added products. Expanding commercial CO2 transport and storage supports the development of a large-scale carbon management industry to reduce emissions, provide new job opportunities, and enhance our energy security.
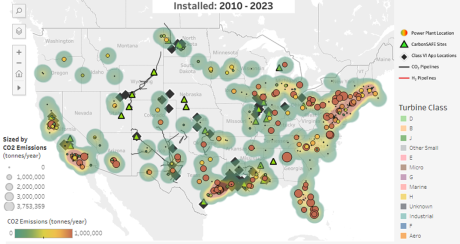
NETL recently published an interactive map showing data on gas turbines installed in the United States from 2010-2023 that tracks trends in installation and annual carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, demonstrating that the Lab’s research and development of revolutionary, near-zero-emissions advanced turbine technology is helping to change the way the nation generates power.
Membrane Technology and Research (MTR) Carbon Capture announced the completion of a carbon capture testing facility at the Wyoming Integrated Test Center (WITC) in Gillette, Wyoming. The facility is the largest membrane-based carbon capture facility in the world. It is designed to capture approximately 55,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year.
In high school, Peter Balash developed a lifelong interest in rugby, and the valuable lessons learned in those hard-hitting matches have guided him throughout his NETL career, helping him recently earn national recognition as an expert and leader in energy economics.
Researchers at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), in a project managed by NETL, developed and demonstrated a new approach for making ordinary Portland cement replacement in concrete that can significantly reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and is already being commercialized for use in U.S. cement plants.
NETL’s research has unlocked a low-temperature synthesis process to make America’s coal waste into critical mineral graphite with a lower processing intensity. This takes what would otherwise be an environmental liability and instead use it to help address rising demand by adding to the domestic supply chain and address commercial market needs for several key industries as well.
Sean Plasynski has been named principal deputy director of NETL.
NETL researchers took a major step forward in studying how well a new solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) product can work in a micro-grid setting when they installed a cutting-edge SOFC system to help meet power needs at NETL’s Morgantown, West Virginia site.
NETL and the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management (FECM) will post a pre-recorded webinar to provide information on the University Training and Research (UTR) Program and a grant writing discussion.