As securing a domestic source of rare earth elements (REEs) remains a priority for the U.S. Department of Energy, a potential opportunity to obtain these elements is within reach thanks to our nation’s abundant coal resources.
With support from the National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL), the Research Triangle Institute (RTI) is exploring methods by which REEs can be extracted, separated, and recovered from coal-based resources.
NETL-supported research to secure a domestic supply of rare earth elements (REEs) shows economic potential regarding efficiency and cost savings and progresses along the pathway to commercial viability.
Many of the nation’s leading scientists and engineers will present new energy technologies at the NETL-hosted Spring Fossil Energy R&D Project Review Meeting Tuesday, April 21, through Thursday, April 23, at the Omni William Penn Hotel in Pittsburgh. The meeting also is expected to attract representatives from electric utilities, as well as research universities and private industries who are interested in partnering with NETL on current and future projects.
As the world continues its transition to a highly tech-driven economy, NETL supports innovative techniques to develop a reliable domestic supply of rare earth elements (REEs), which are vital materials for modern technologies. To that end, NETL is collaborating with the University of Kentucky and their subcontractor Virginia Tech to demonstrate a novel process that could see America’s coal country as a new supplier of these vital materials.
Innovations by researchers at Ohio State University have shown potential to deliver a supply of strategically and economically vital rare earth elements (REEs).
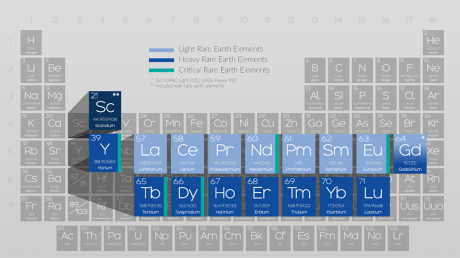
REEs are used in everything from green energy applications and personal electronics to defense technology and smart car systems. Important as these elements are, China controls the lion’s share of the world market.
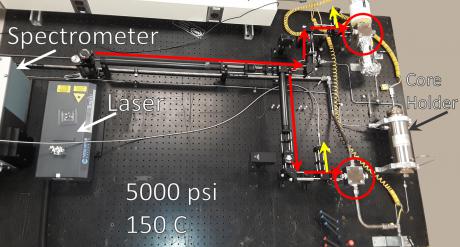
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, or LIBS, is a rapidly advancing analytical technique that provides a cost-effective, quick and precise method for determining the elemental composition of any solid, liquid or gas sample.
To really understand a complex challenge, it pays to take a close look at the details. NETL researchers are taking this approach as they use X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to understand and characterize rare earth oxides on the atomic level. The pioneering research was recently selected for publication in the June edition of the journal Surface Science Spectra. To view the study, go here.
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and NETL have announced up to $87.3 million in federal funding for cost-shared research and development (R&D) projects for advanced coal technologies and research. DOE Assistant Secretary for Fossil Energy Steven Winberg announced this R&D funding at the Annual Project Review Meeting for Crosscutting, Rare Earth Elements, Gasification, and Transformative Power Generation at the National Energy Technology Laboratory.
The National Energy Technology Laboratory’s (NETL) Regional Workforce Initiative will present a free Energy 101 Webinar at 1 p.m. Thursday, March 28. The on-line event is designed to inform participants about evolving technology solutions related to rare earth elements (REEs) and advanced composites/materials and manufacturing and their potential economic development impact on the Appalachian Region.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Fossil Energy (FE) has issued a Notice of Intent (NOI) for a Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) focused on recovering rare earth elements (REE) and critical materials (CM) from domestic coal resources, using novel and conventional extraction, separation, and recovery processes.